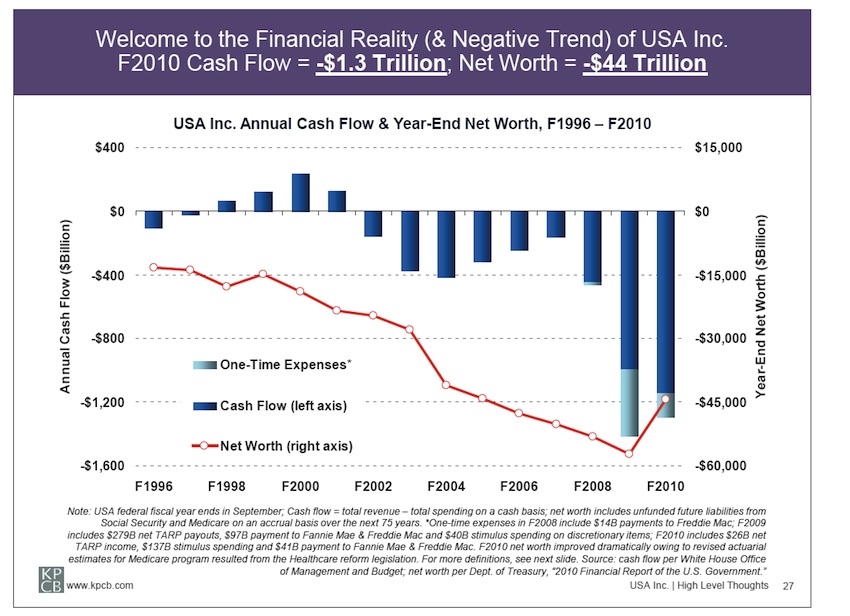
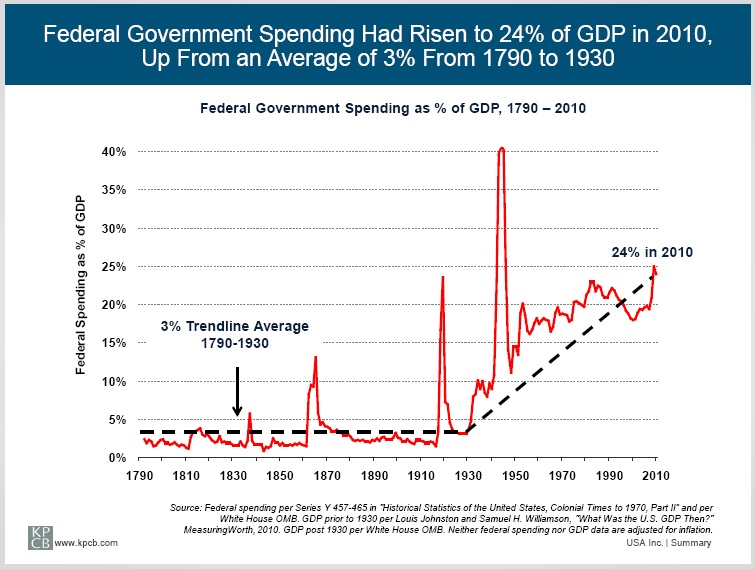
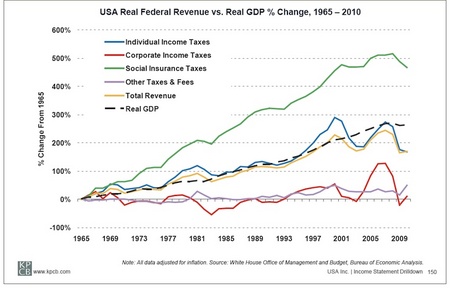
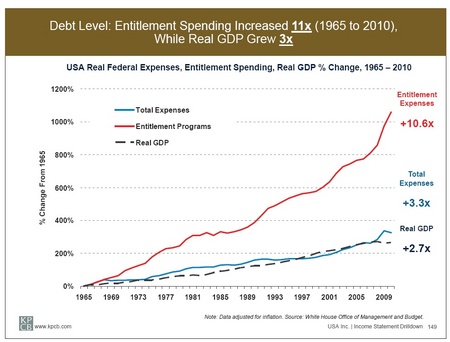
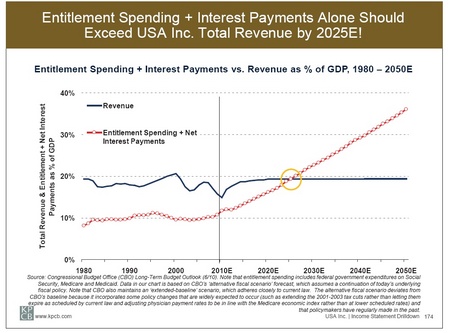
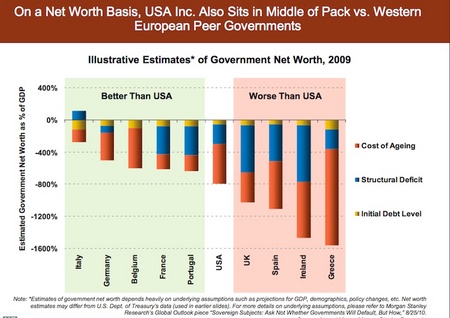
Coolidge was more concerned with domestic issues than foreign policy. This had been true of most US presidents since the Civil War until 1917 and it was part of Harding’s “Return to Normalcy” plan. Coolidge knew little about other countries although he was not an isolationist. The true isolationist policy of the US was in the 1930s under Roosevelt who canceled a Hoover sponsored economic summit in Britain as soon as he was inaugurated. Only in 1939 and 40 was Roosevelt converted to the internationalist that is remembered by his supporters and biographers, internationalists themselves. I will have more to say about the slanders of Harding and Coolidge by the political left and the historians later.
Coolidge’s domestic agenda was dominated by a few issues. The first was the emergence of the “Farm Bloc” in Congress. The McNary- Haugen bill was the first of the “farm relief” bills and would dog Coolidge through his presidency as he vetoed it but it kept coming back as the farm bloc grew stronger. The background of the bill is well stated in the Wikipedia article:
World War I had created an atmosphere of high prices for agricultural products as European nations demand for exports surged. Farmers had enjoyed a period of prosperity as U.S. farm production expanded rapidly to fill the gap left as European belligerents found themselves unable to produce enough food. When the war ended, supply increased rapidly as Europe’s agricultural market rebounded. Overproduction led to plummeting prices which led to stagnant market conditions and living standards for farmers in the 1920s. Worse, hundreds of thousands of farmers had taken out mortgages and loans to buy out their neighbors property, and were now unable to meet the financial burden. The cause was the collapse of land prices after the wartime bubble when farmers used high prices to buy up neighboring farms at high prices, saddling them with heavy debts. Farmers, however, blamed the decline of foreign markets, and the effects of the protective tariff. They demanded relief as the agricultural depression grew steadily worse in the middle 1920s, while the rest of the economy flourished.
As the 1920s went on and Europe recovered, the rationale for the bill was less and less credible. Eventually, it would be the basis for the Roosevelt farm policy and has survived in some form until the present. The basic mechanism of the bill was to establish high tariffs for foreign farm products. The high tariffs on manufactured goods were the worst aspect of Republican policies in the 1920s and contributed to the financial instability that led to the crash in 1929. Europe could not sell to the US because of the tariffs and so could not generate the revenue to repay the war loans. That is an oversimplification but it was a factor. The farm bill would add price supports (equal to the tariff on imports) on farm exports to keep prices high. The government organized cooperatives would sell to foreign buyers at the lower world price and the difference would be collected as a tax or “equalization fee” on domestic sales of each export commodity. This would keep US food prices higher than the world price. We see something very much like this in sugar subsidies and in the ethanol tariff the prevents fuel companies from buying cheap Brazilian ethanol.
Coolidge supported a different approach which included rural electrification, modernization of farming with better hybrid seeds and better business methods. I should add that my own family were farmers in Illinois during this period. One farm family sent their son to agricultural college in the 1920s to the amused derision about going to college to learn how to farm from my grandfather. He returned home, revolutionized farming methods in Illinois with fertilizers, hybrid seed and crop rotation and his children now own most of the farmland where my ancestors once lived. Few Congressmen knew anything about farming and Coolidge’s approach did not stop them from sponsoring the tariff bill every year or two. He vetoed it twice.
Another major issue was the Ku Klux Klan. This was more of a problem for Democrats with their base in the “solid South” but it affected Republicans, as well. The Klan in the 1920s was unrelated, except in name, to the organization founded by Nathan Bedford Forrest after the Civil War. The “second Klan” did include some Republicans and was more concerned with immigration and anti-Catholic and anti-Jewish bigotry, both related to immigration. It had been founded in Atlanta in 1915 by Colonel William Simmons. Its attraction was in its pro-farmer and pro-poor native born Americans sympathies. It was anti-Wall Street and had more geographic diversity with active members in Oregon and California as well as in Maine and New York. A Texas Senator and an Indiana Senator were members and a number of governors, including in California and Oregon, had received Klan support. It had about 4 million members at its peak. The GOP convention had a proposed anti-Klan plank in the platform and that would be a fight when the time came.
Prohibition was a disastrous progressive experiment whose pathologies were becoming apparent in 1924. Coolidge said that Congress had passed the law and he would support it but he also added, “Any law that inspires disrespect for other laws– the good laws– is a bad law.” A number of organizations were formed to oppose the Volstead Act as the corruption and lawlessness grew. In support, there was actually a Prohibition Party, which held its convention on the day before the GOP convention and nominated candidates for president and vice-president. As previously noted, a number of Progressives had returned to the Republican Party in 1920 and they also constituted a Prohibition wing of the party. Hiram Johnson had shown how powerful they could be by denying Charles Evans Hughes the presidency in 1916.
Coolidge was more pro-civil rights than Harding had been but it has been largely forgotten in this country that the Democrats were the party of segregation. Woodrow Wilson had segregated the civil service in 1914 after it had been integrated since 1865. Coolidge gave the Commencement Address at all-black Howard University on June 6. He spoke of the progress of American blacks since the Emancipation Proclamation. He noted that, “in 1863, there were four million black Americans, 12 thousand of whom owned their own homes.” “In a little over half a century since, the number of business enterprises operated by colored people has grown to nearly 80,000, while the wealth of the negro community has grown to nearly $ 1,100,000,000.” He continued with a list of material and intellectual progress made since that point. He added, referring to the war, “The propaganda of prejudice and hatred which sought to keep the colored man from supporting the national cause completely failed. The black man showed himself the same kind of citizen, moved by the same patriotism, as the white man.”
The 1924 Convention opened in a placid mood on June 10. Coolidge was in control. Henry Cabot Lodge was a simple delegate and powerless. The country and the party had moved on. The power of the bosses was much diminished from 1920 and many of them were dead. Radio was breaking down the regionalism of the country just as it would eventually dilute regional accents. The Convention was the first to be broadcast on radio, a concept that did not even exist in 1920. The final platform did not mention the Klan but did congratulate the party for the improvement in economic conditions since 1920. They came out in favor of higher agricultural tariffs but not the McNary- Haugen bill. There was no mention of Prohibition or race relations. There was widespread concern that LaFollette would make a third party race on the Progressive ticket.
The Leopold-Loeb murder case competed with the Convention for public interest and newspaper coverage. The only uncertainty was the vice-presidential nomination. There were many names considered. Coolidge, through an intermediary, approach William Borah to determine his interest in joining the ticket. Borah, certain of his superior talents compared to Coolidge asked, “At which end?” Another bit of Washington gossip at the time was that Borah was the real father of Alice Roosevelt Longworth’s only child, daughter Pauline. Alice was none too discreet and Borah had a reputation for womanizing so the child was often called ” Aurora Borah Alice,” among the cognoscenti.
Coolidge favored a former Senator from Iowa and federal judge named William S. Kenyon. Kenyon had been a member of the Farm Bloc and a very astute opponent of Harding within the party. He was a progressive but had supported Taft in 1912 and was considered a “regular” although he was pledged to Hiram Johnson at the 1920 convention. Harding had offered him a federal judgeship to get rid of him from the Senate and Kenyon accepted but then became the judge who threw out the Tea Pot Dome oil leases and criticized Harding about the affair. Kenyon was a Coolidge supporter and would have made an interesting VP nominee. The Progressives would be pleased and might be lured from LaFollette if he ran. Unfortunately, Kenyon was not interested. The next candidate was Lowden, who was an excellent reform governor of Illinois and a serious presidential candidate in 1920. He also declined. The convention finally turned to Charles G Dawes, a banker who had an international reputation (and a Nobel Peace Prize) for his “Dawes Plan” for trying to deal with the reparations nightmare.

Dawes nomination was another example of serendipity as the man asked to nominate him agreed to do so because he wanted to run for the Senate in Nebraska and this would give him a chance to be heard in Nebraska on a national broadcast. A W Jefferis was a Nebraska delegate and not particularly a friend of Dawes. The radio in 1924 was a technological wonder and instant fame followed such an opportunity. Dawes was a bit of an independent politically. He had recovered from financial wipe-out in the Panic of 1893 and was Comptroller of the Currency under McKInley in 1901, which position he resigned to run unsuccessfully for the Senate. He served in the Army during World War I as head of the General Purchasing Board and ended the war as a brigadier general. He then took charge of the body responsible for liquidating the American supplies remaining in France at the end of the war. He became famous for his testimony before a House Committee on War Expenditures. The Republican majority was attempting to show that the Democratic Administration had been profligate in purchasing, if not dishonest. Dawes, of course, had been in charge of the purchasing and was outraged in spite of his Republican credentials. He became infuriated with the committee members’ ignorant questions and allegations of profiteering. His scathing and witty answers to the committee made him famous with the public. He was headline news the next day.
Dawes was a man of many talents. He played several instruments and composed music, including a piece in 1911 that eventually, with words, became the song “It’s All in the Game,” in the 1950s. After the 1920 election, he turned down the Secretary of the Treasury position but accepted the new position of Director of the Bureau of the Budget. The Coolidge tax cuts and the Dawes budget controls resulted in the government showing a budget surplus in each year of the Harding-Coolidge presidency. The Bureau of the Budget continued to control government expenditures until reorganized by John Kennedy in 1961. In 1923, Dawes was asked to join a Committee of Experts to rescue the German economy. The result was the Dawes Plan and the 1925 Nobel Peace Prize. Dawes was an outstanding choice for the vice-presidency. Coolidge, who hated to campaign, was greatly complemented by Dawes who enjoyed it.
Meanwhile, the Democrats imploded at their convention over issues like Prohibition and the Klan. The early favorite was Wilson son-in-law William McAdoo. He had an attractive resume but two glaring problems. He was supported by the Klan, although not a member, and he was a “dry.” His principal opponent, Senator Oscar Underwood of Alabama was a “wet” and a fierce opponent of the Klan. He privately believed racism was responsible for much of the poverty of the South. The Klan was powerful in the Democratic Party and Underwood had opposed Women’s Suffrage and Prohibition, both positions unpopular in 1920. Al Smith, Governor of New York, had not entered primaries and knew that the convention decision would depend on the issues of the Klan and Prohibition. Smith’s Catholic religion would also be a huge factor in the election if he were nominated, as he was in 1928. The Convention was to be held in New York, which encouraged Smith’s ambitions.
One of the first nominating speeches, by Forney Johnson of Alabama, speaking on behalf of colleague Underwood, threw down the gauntlet on the Klan. Like Underwood, Johnson was a fierce opponent of the Klan and his speech tore the convention apart. Live radio coverage magnified the effect. A motion to condemn the Klan failed by a single vote. The one positive development was Franklin Roosevelt’s nominating speech for Al Smith, the “Happy Warrior.” It marked Roosevelt’s return to the public scene after his polio rehabilitation. He had been the VP nominee in 1920. After 50 ballots, delegates talked of returning home without a nominee. Smith allies hooted from packed galleries and on the 100th ballot he led with about third of the delegates. Eventually,
on the 103rd ballot, the delegates turned to John W Davis, a distinguished lawyer and former Congressman and his VP nominee, Charles W Bryan Governor of Nebraska. Bryan was the younger brother of William Jennings Bryan, perennial Democratic nominee, famous for his populist politics and his “Cross of Gold” speech.

The Bryan brothers, ever hopeful.
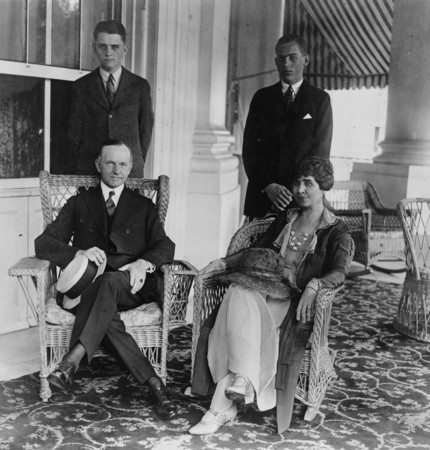
The Democrats were crushed in the election but personal disaster struck Coolidge. On June 30, while playing lawn tennis with his brother, Calvin Jr developed a blister on his toe from playing without socks. He was 16 years old. The blister became infected and he died on July 7, 1924. His father never recovered. My son, who is diabetic, developed a similar blister on his toe when wearing firefighter boots. He works 72 hour shifts and, by the time he finished his shift and went to an urgent care center, he had positive blood cultures. He was hospitalized for several weeks and had a one year recovery including skin grafts and multiple surgeries. He is now back at work but, even with modern antibiotics and other measures, he was very ill and took a long time to recover. Calvin Jr was not diabetic but there were no antibiotics available and sepsis was a fatal complication.
Dawes and Coolidge had dinner together during the boy’s illness. Dawes had lost a 21 year old son to drowning in 1912 and understood the president’s concern although he did not realize the seriousness of the illness yet. As he left, he looked into Calvin Jr’s room. “As I passed the door of Calvin’s room, I chanced to look in. He seemed to be in great distress. The president was bending over the bed. I think I have never witnessed such a look of agony and despair that was on the president’s face.” We forget what the days before antibiotics were like. In the very early days of the development of penicillin, one of Howard Florey’s first patients was a policeman who had pricked his finger on a rose thorn. He was dying of streptococcal sepsis, the same infection that undoubtedly killed Calvin Jr. The amount of penicillin they had been able to isolate was very small. They treated the policeman and he improved but then they ran out of the drug. They tried everything including extracting it from his urine but could not get enough and he died.

Calvin Jr with hanging tobacco leaves.
The president agonized about his lost boy. He signed a book for friend who had also lost a son. “To my friend, in recollection of his son, and my son, who by the grace of God have the privilege of being boys throughout eternity.” Calvin Jr had had a previous serious illness, at age six years old, and required surgery to drain an empyema, a collection of pus in the chest following pneumonia. His father was very worried then, as well, but things turned out well. There is another story of this time in Coolidge’s life. Colonel Starling, the president’s Secret Service bodyguard, on his way into the White House, saw a small boy standing outside the railing looking in. “I asked him what he was doing up so early. He looked up at me, his eyes large and round and sad. I thought I might see the president,” he said. “I heard that he gets up early and takes a walk. I wanted to tell him how sorry I am that his little boy died.” “Come with me, I’ll take you to the president,” I said. He took my hand and we walked into the grounds. In a few minutes, the president came out and I presented the boy to him. The youngster was overwhelmed with awe and could not deliver his message so I did it for him. The president had a difficult time controlling his emotions. When the lad had gone and we were walking through Lafayette Park, he said to me: “Colonel, whenever a boy wants to see me, always bring him in. Never turn one away or make him wait.” There has been considerable speculation, based on some evidence, that the boy’s death left Coolidge in a prolonged depression that affected his presidency.
To be continued