I recently read a book titled, The 10,000 Year Explosion.
Its premise is that evolution did not stop or “pause” with the development of modern man 40,000 years ago.
A few basic facts about genetics. Genes are sets of nucleotides that encode proteins by encoding RNA. This is all in my book, A Brief History of Disease, Science and Medicine. One key fact is that:
Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits.
I discussed this at some length two years ago and then, because it stirred a hornets nest at Ricochet, I posted some of the nasty replies here.
Mutations occur at random or under the influence of outside influence like UV radiation. Some are harmful, like cancer, and are not continued in the “gene pool.” Some are beneficial and may persist as they provide an advantage to the individual who may live longer, have more children and have more of the children survive to reproduce.
Humans evolved in Africa and spread outside of Africa before 50,000 years ago. There have been successive waves of modern humans that were better adapted to life, especially in areas that were new and often inhospitable like Ice Age Europe. One such group was called the “Neanderthal, as they were found in the Valley of the Neander River in Germany.
Neanderthals came to Europe some 300,000 years ago. They hunted big game with stone tools. Their territory spanned Europe and Asia. They left distinctive “Mousterian” artefacts.
There were other groups and we are starting to find out who and what they were from their DNA.
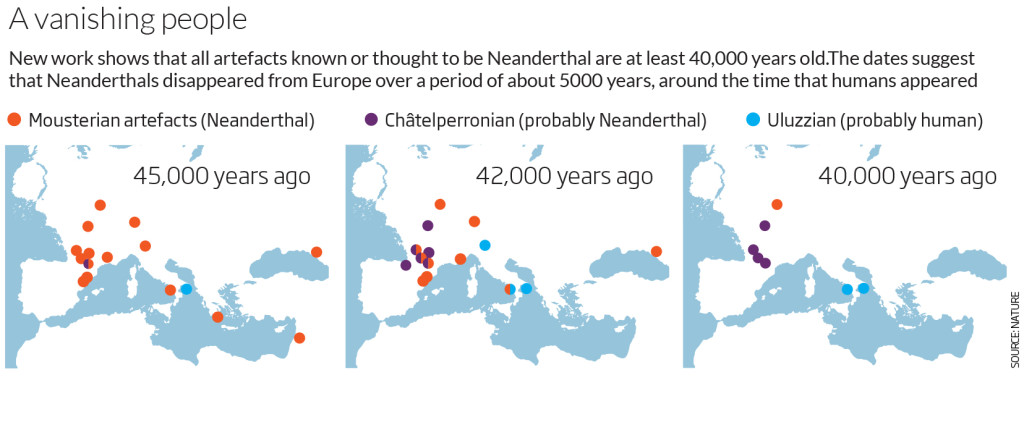
We know that modern humans first arrived in Europe about 45,000 years ago when the continent was still a Neanderthal stronghold. Over the next 30,000 years – archaeological work has revealed – a procession of different cultures, each associated with different artefacts and lifestyles, rose in Europe.
Archaeologists tend to think these sort of cultural shifts reflect the spread of new ideas through an unchanging population. But a new analysis of nuclear DNA taken from 51 ancient Eurasians tells a different story. They actually reflected the spread of different peoples.
The Neanderthals were gone earlier than recently believed.
“Until recently, I and many with me had thought that Neanderthals survived until 30,000 years ago, or perhaps even slightly later,” says Svante Pääbo of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany. “The new dates make it clear that they disappeared 10,000 years earlier.”
What happened ?
For Pat Shipman of Penn State University, this supports her theory that modern humans acted like an invasive species in Europe, beating the Neanderthals in a competition for resources. That’s a “distinct possibility”, Higham says.
But that does not mean we murdered our cousins. There is no evidence humans ever killed Neanderthals, and they probably didn’t meet often, says Higham.
So what role did we play? Many now suspect we were the last straw for an already fragile species. Genetics suggests Neanderthal numbers dropped sharply around 50,000 years ago. This coincides with a sudden cold snap, hinting climate struck the first blow.
The Ice Ages were a huge stress.
Over the next 30,000 years – archaeological work has revealed – a procession of different cultures, each associated with different artefacts and lifestyles, rose in Europe.
Archaeologists tend to think these sort of cultural shifts reflect the spread of new ideas through an unchanging population. But a new analysis of nuclear DNA taken from 51 ancient Eurasians tells a different story. They actually reflected the spread of different peoples.
Some of this change involved breeding with Neanderthals, and many of us (including me) have some Neanderthal DNA. Why ? The Neanderthals might have been better adapted to Ice Ages which waxed and waned.
During this period, there were several changes between glacier advance and retreat. The Last Glacial Maximum, the maximum extent of glaciation within the last glacial period, was approximately 22,000 years ago. While the general pattern of global cooling and glacier advance was similar, local differences in the development of glacier advance and retreat make it difficult to compare the details from continent to continent (see picture of ice core data below for differences).
From the point of view of human archaeology, it falls in the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods. When the glaciation event started, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa and used tools comparable to those used by Neanderthals in Europe and the Levant and by Homo erectus in Asia. Near the end of the event, Homo sapiens spread into Europe, Asia, and Australia.
Maybe Neanderthals were better adapted to glacial epochs.
The Aurignacian culture was dominant between about 45,000 and 35,000 years ago. This culture produced fine bone and stone tools, and some of Europe’s oldest and most beautiful art – for instance at Chauvet cave in southern France.
By about 33,000 years ago a new culture that began in south-east Europe was beginning to spread across the continent: the Gravettian. This is famous for big-game hunting of mammoths and bison.
And later, at the height of the Ice Age about 19,000 years ago, yet another culture swept across west and central Europe. This Magdalenian culture is famous for its reindeer hunts and for its artwork, carved into bones and antlers.
One of the oldest individuals examined by David Reich at Harvard Medical School in Boston and his colleagues is represented by a thigh bone found at a site called Goyet cave in Belgium. Radiocarbon dating shows it is 35,000 years old, meaning the Goyet individual is associated with the Aurignacian industry.
Now, it appears that these people were quite different genetically.
the Aurignacians were pushed aside by an expanding wave of Gravettians.
“It is exciting and striking how a relatively homogeneous population sweeps across large parts of Europe between 33,000 and 26,000 years ago, displacing the populations that were there before,” says Reich.
But that’s not the full story. The genetic analysis also looked at six Magdalenians: they are descendants of the displaced Aurignacians.
This is a real surprise, says team member Cosimo Posth at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena, Germany. It shows that the Aurignacian lineage didn’t disappear when the Gravettians swept across Europe.
“In fact from the end of the Last Glacial Maximum some 19,000 years ago, its genetic component reappeared in Spain. From then to around 14,000 years ago this nuclear signal spread in Europe again,” he says.
They may have been pushed into a cul de sac in Spain but returned as the glaciers retreated. Why ?
We know a few things, such as why white skin evolved. As humans moved from Africa to Europe and faced cold climates, they needed Vitamin D which is synthesized in the skin.
Dark skin is useful and provides and evolutionary advantage in tropical settings. It also has some protective effect on sun burning and skin cancer. One negative consequence of inadequate Vitamin D is Ricketts, a disease of bones.
Rickets is defective mineralization or calcification of bones before epiphyseal closure in immature mammals due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D,[1] phosphorus or calcium,[2] potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries.
This provides a strong feedback for selecting beneficial mutations.
Some of this will lead to modern therapy and that is why I wrote that I would not recommend a student for medical school who did not believe in evolution. Here is some of the negative response I got. I quit Ricochet when my subscription expired.